What is the internet of things?
IoT technology is a collection of connected things able to communicate with one another.
Part of our Internet of Things briefing
Global | Publication | June 2019
IoT technology is a collection of connected things (such as sensors) able to communicate with one another (or with a central system) without human involvement (whether human-to-human or human-to-computer). The use of the word “Internet” in the term “Internet of Things” connotes connectivity of some kind, although such connectivity need not be via the traditional Internet (for example, it could be via telephony – in particular, the advent of 5G will do much to foster the growth of mobile IoT technology). Connectivity and things are, however, only part of the IoT landscape. IoT technology is therefore best described not in terms of connected things per se, but as an ecosystem made up of various layers.
The diagram below to show the component parts and functions.1 When the devices and other elements described below operate with each other, they together form the Internet of Things.
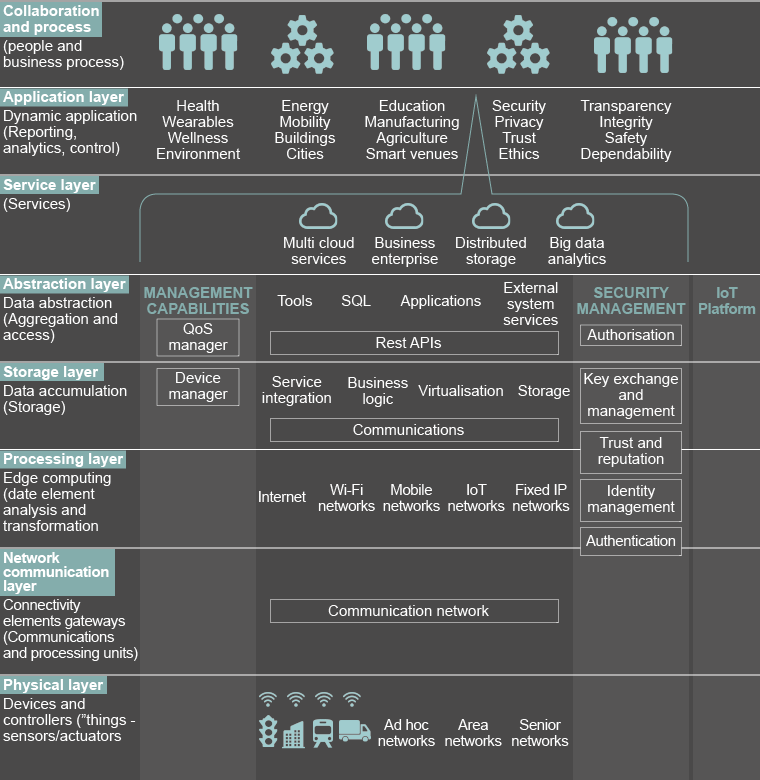
Incorporation of people and business processes: action taken
Adding value: the information from the previous layers only provides added value (for example, contextual awareness of surroundings) when an action is undertaken or insight gained
People or processes are involved in order to make improvements
The services provided by the Service Layer, the Application Layer and the Collaboration and Processes Layer are typically provided together in a single IoT cloud platform
Reporting and analysis: reporting, analysis and controlling of data
Front-end interface: with the user
Ensures that users can interact and understand the underlying data
Data interpretation: in order to obtain insights
Processing of data: giving meaning to the data
Provides the service of being able to interpret the data in the Application Layer
Data scaling: data needs to be “scaled” to a higher level
Data rendering: allows data to be “rendered” and stored in a way that enables the development of simpler and performance-enhanced applications
Multiple storage systems may be required for data scaling
Functions
Data accumulation: networks need to move data through the network. Storage is required to achieve this
Data conversion: converts data in motion to data at rest. As a result, data is available to be used by applications
Storage technologies typically used include:
Data conversion: converts data flows from the network into information suitable for storage and processing
Processes: the ability to process and act on events based on information collected by the sensor and actuator capabilities in the Physical Layer
Cloud services: hosted in the Internet
Processing can occur within the cloud
Gateways: alternatively processing may occur within so-called gateways connecting the devices and the broader Internet. Gateways may provide transmission security (encryption), protocol interoperability (data flows), data storage and analysis (transforming raw data into something more meaningful) and local event processing (for example, activating an actuator)
Gateways may be provided by:
Information transmission: communications and connectivity
Devices: between devices and the network
Network: across the network
Connection to processing: between the network and low-level information processing in the Processing Layer
May include the following forms of connectivity:
The hardware: or “things” – the core of IoT physical infrastructure
Data: captures, processes and transmits data
User interface: through which user interacts
May include the following depending on size constraints:
Connectivity: transmission and receipt of data to/from other devices over the cloud
Various network communication options (see Network Communications Layer)
Sensors: a device that converts variations in a physical quantity, such as pressure, into an electrical signal
May include detection of:
Actuators: accept a digital signal and produce a physical change
May trigger or change the following:
Device computing and storage: low electricity-consuming processing and data storage
Functionalities may include, or depend on:
IoT technology is a collection of connected things able to communicate with one another.
IoT platforms provide services that have, as their primary focus, the exploitation of data existing at the higher layers of an IoT ecosystem.
Addressing the economic, sectoral and geographical impacts of IoT.
Like all information technology, IoT technology is not immune from technology-related vulnerabilities.
The IoT device manufacturing industry is characterised by a relative lack of product lifecycle plan.
Considerations include privacy and cybersecurity, IP rights, liability and autonomous decision making issues, regulatory and competition, tax and litigation.
Businesses wishing to utilize IoT will need to consider a number of issues.
IoT stakeholders should be reviewing their privacy policies and terms and conditions.