What is the internet of things?
IoT technology is a collection of connected things able to communicate with one another.
Part of our Internet of Things briefing
Global | Publication | June 2019
Spend projection: global spending on IoT technology is projected to be at a CAGR of 15.6% until 2020. This would result in a global investment in IoT of USD 1.6 trillion.1
Number of things: between six and fourteen billion devices (not including mobile phones, tables, computers and other remotes) are currently connected via some form of communications network.2 By 2020 it is estimated that there will be twenty billion internet connected devices worldwide.3
Who is deploying IoT?: businesses on a B2B basis have the greatest share of IoT investment, growing to USD 832 billion in 2020. Using a so-called “Industrial Internet of Things”, industries that are expected to invest the most in IoT by 2020 are manufacturing, transportation and utilities.4 The networks and data that arise in relation to the IoT ecosystem will support an enormous range of economic activities. The following shows projected full-scale IoT deployment by industry:
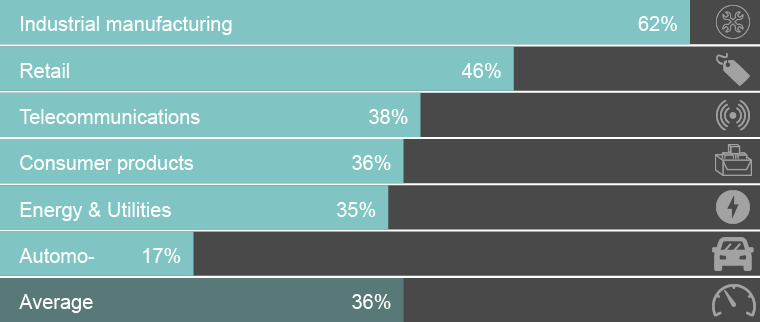
Source: Gapgemini, Unlocking the Business Value of IoT in Operations, 2018, page 4
Where is IoT technology being deployed?: IoT full-scale deployments show marked geographical variation:
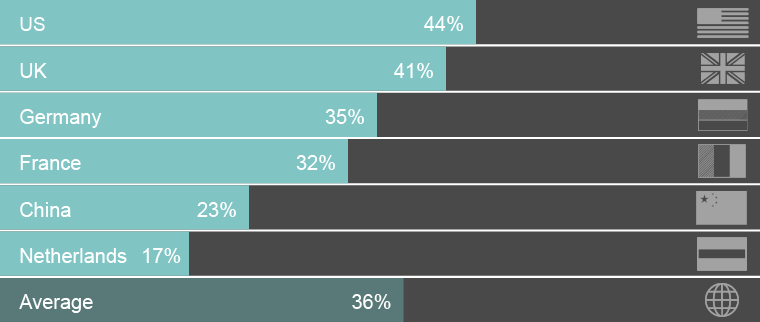
Source: Gapgemini, Unlocking the Business Value of IoT in Operations, 2018, page 5
IoT technology is a collection of connected things able to communicate with one another.
IoT platforms provide services that have, as their primary focus, the exploitation of data existing at the higher layers of an IoT ecosystem.
Addressing the economic, sectoral and geographical impacts of IoT.
Like all information technology, IoT technology is not immune from technology-related vulnerabilities.
The IoT device manufacturing industry is characterised by a relative lack of product lifecycle plan.
Considerations include privacy and cybersecurity, IP rights, liability and autonomous decision making issues, regulatory and competition, tax and litigation.
Businesses wishing to utilize IoT will need to consider a number of issues.
IoT stakeholders should be reviewing their privacy policies and terms and conditions.